EYWA Data Transport Script
This use case will utilize the fact that EYWA itself is created and modeled using EYWA. EYWA has an option to import and export datasets modeled in it. This means that the dataset models can be shared between different EYWA instances no matter where they are installed. However, it will only import/export the model, not the actual data that is stored in it.
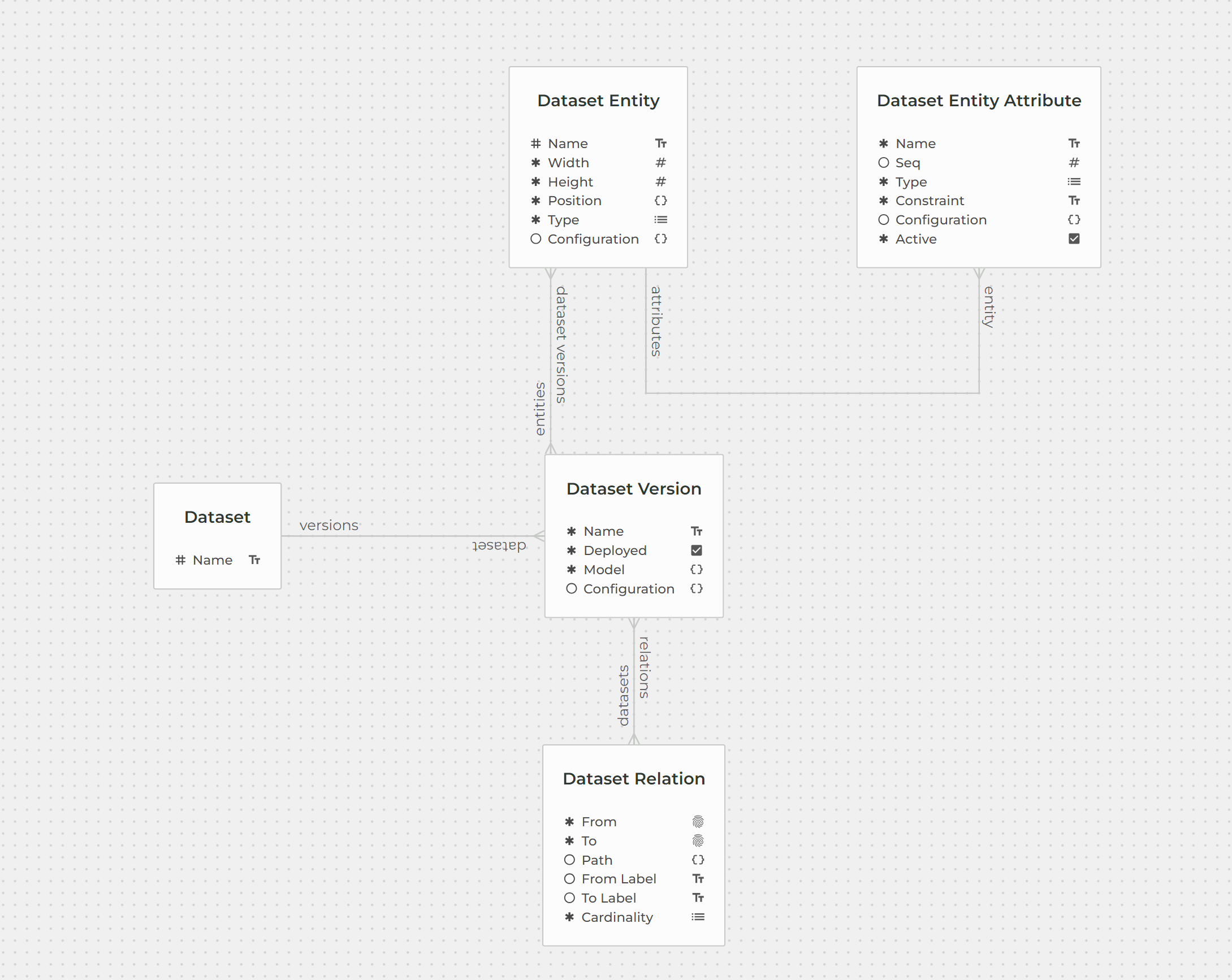
Every dataset that is created in EYWA is described by Datasets dataset. Using the Datasets dataset we can get all the information we need to generate Graphql mutations and queries that will import and deploy certain dataset and export/import from/to EYWA actual data.
Importing and Deploying a Dataset#
Reading a .edm file#
EYWA exports datasets into the .edm file. Also, when importing, EYWA expects the .edm file. The content of these files is in JSON format that includes name and euuid of the dataset, dataset version, dataset version name and model.
Then the first step when importing a dataset is to read the .edm file. Since the contents of the file are in the JSON format we'll use json.loads(). Below is the function that reads a .edm file
def read_edm_file(file_path:str) -> dict: ext = os.path.splitext(file_path)[1] if ext != ".edm": raise ValueError(f'The extension of the import file must be ".edm" but it is "{ext}"!') with open(file_path, 'rb') as f: file_contents = f.read() file_text = file_contents.decode('utf-8')
return json.loads(file_text)Importing a dataset#
Now we can import the dataset. To import the dataset we can use stackDataset and stackDatasetVersion stack mutations. To actually execute these mutations eywa.graphql() function from eywa-reacher-client is used. Below is the function that accepts data from the .edm file as an argument and imports said data to EYWA.
def add_dataset(data:dict) -> tuple[dict, dict]: version_euuid = str(uuid.uuid4()) data["~:dataset"]["versions"] = [{'euuid': version_euuid}] stack_dataset_data = {key.replace("~:", ""): (value.replace("~u", "") if isinstance(value, str) else value) for key, value in data["~:dataset"].items()} model = json.dumps(data["~:model"], ensure_ascii=False) stack_dataset_version_data = { 'euuid': version_euuid, 'name': data["~:name"], 'deployed': data["~:deployed"], 'model': model }
stack_dataset_mutation = "mutation($var:DatasetInput!){stackDataset(dataset:$var){euuid}}" stack_dataset_version_mutation = "mutation($var:DatasetVersionInput!){stackDatasetVersion(dataset_version:$var){euuid}}" eywa.graphql({'query': stack_dataset_mutation, 'variables': {"var": stack_dataset_data}}) eywa.graphql({'query': stack_dataset_version_mutation, 'variables': {"var": stack_dataset_version_data}}) return stack_dataset_data, stack_dataset_version_dataDeploying a dataset#
After the dataset is imported it can finally be deployed! To deploy a dataset there is a special mutation deployDataset. It takes DatasetVersionInput as an argument. Below is a function that deploys the dataset:
def deploy_dataset(dataset_data:dict, dataset_version_data:dict) -> None: if "versions" in dataset_data.keys(): del dataset_data["versions"] if "deployed" in dataset_version_data: del dataset_version_data["deployed"] dataset_version_data["dataset"] = dataset_data dataset_version_data["model"] = dataset_version_data["model"].replace(r'\"', r'"') mutation = """mutation($var:DatasetVersionInput){\n deployDataset(version:$var) {euuid}}"""
response = eywa.graphql({'query': mutation, 'variables': {"var": dataset_version_data}})Final functions that imports and deploys a dataset#
The final import_dataset() function that reads the data from .edm file, imports the dataset from the .edm file and finally deploys said dataset, looks like this:
def import_dataset(edm_path:str) -> None: data = read_edm_file(edm_path) dataset_data, dataset_version_data = import_dataset(data) deploy_dataset(dataset_data, dataset_version_data) Exporting Data#
Get dataset entities and relations#
To export data from EYWA to .json file, the dataset name and version must be specified (as well as a path to the .josn file where the data will be stored). Using the dataset name and version we can get information about all the entities and relations contained in that dataset. Function below queries Datasets dataset using the search query to get that information:
def get_dataset_info(dataset_name:str, dataset_version:str) -> dict: query = f"""{{searchDatasetVersion{{ dataset {{name(_eq:"{dataset_name}")}} name(_eq:"{dataset_version}") relations{{ euuid from_label to_label cardinality from to }} entities{{ euuid name attributes{{ name type }} }} }}}}""" response = eywa.graphql({"query": query, "variables": {}})["data"]["searchDatasetVersion"] if not response: raise ValueError(f'There is no dataset named "{dataset_name}" with version {dataset_version}') return response[0]Using the information about the datasets' entities and relations that we got from EYWA, we can construct a new query for each entity and for each relation tied to that entity. Below is the function that takes information about a dataset as an arguments and constructs a query:
Construct a query for every entity#
def construct_query_for_export(dataset_info:dict): entities = dataset_info["entities"] relations = dataset_info["relations"]
query = "{" for entity in entities: query += "\nsearch" + entity["name"].replace(" ", "") + "{\n" query += get_attributes_string(entity) entity_relations = [rel for rel in relations if rel["from"]==entity["euuid"]]
for rel in entity_relations: neighbour = [ent for ent in entities if ent["euuid"]==rel["to"]] for n in neighbour: query += "\n" + rel["to-label"].replace(" ", "_") + "{\n" + get_attributes_string(n) + "\n}"
query += "\n}" query += "\n}" return queryAfter executing the constructed query, EYWA returns all the data that is stored in the dataset. The last step is to save that data into .json file:
Write data to .json file#
def write_to_json_file(data:dict, json_path:str): replace_dash_with_underscore(data) with open(json_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as json_file: json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4)Below is the final function that takes dataset name, dataset version and path to the .json file where data will be saved, as arguments and exports all the data stored into the .json file:
Final functions that exports data#
def export_data(dataset_name:str, dataset_version:str, export_file_path:str) -> None: dataset_info = get_dataset_info(dataset_name, dataset_version) query = construct_query_for_export(dataset_info) response = eywa.graphql({"query": query, "variables": {}}) write_to_json_file(response["data"], export_file_path)Importing Data#
The simplest function of all is for importing data. It takes a path to the .json file that contains data as an argument, creates a stack mutation for every top-level key in the file and executes the mutation to insert data into EYWA.
Final function that imports data#
def import_data(import_data_path:str) -> None: data = read_json_file(import_data_path) for query_name in data.keys(): query_subject = re.search(r"[A-Z].*", query_name) if not query_subject: raise ValueError(f'Could not find query subject in string "{query_name}"') query_subject = query_subject.group(0) mutation_variable = data[query_name] mutation_name = "stack" + query_subject + ("List" if isinstance(mutation_variable, list) else "") mutation = "mutation($var:" + \ (f'[{query_subject}Input!]' if isinstance(mutation_variable, list) else f'{query_subject}Input!') + \ f'){{{mutation_name}({camel_to_snake(query_subject)}:$var){{euuid}}}}' eywa.graphql({"query": mutation, "variables": {"var": mutation_variable}}) JSON FILE
This function expects that .json file is formatted similarly as .json file that is created while exporting data using this script. Which means that it expects that the top-level keys are the names of the queries used to search entities (i.e. searchUser or getUser).